How To Repair A Refrigerator That Keeps Running
- Rated as EASY
- 2772 repair stories
- 7 step by step videos
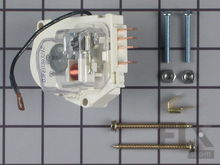
Defrost Timer
When your compressor’s been running a total of eight to ten hours – that’s about every day or two days – a mechanical defrost timer will start a defrost cycle, shutting down the compressor for 20-30 minutes to allow the evaporator be defrosted by the defrost heater. So if the defrost timer is malfunctioning, the compressor may not be running its cycles correctly. Depending on your model, you might find the defrost timer behind the kick plate at the bottom front of the fridge; as part of the control panel in the main body of the fridge where the food is kept fresh; or in a side-by-side unit it might be in the back. Unplug the fridge, and locate the terminals on the defrost timer upon which to perform continuity checks for the motor or the switch. If it’s a mechanical timer instead of an electronic one, you can advance it yourself with a simple screwdriver while the fridge is running. Insert the blade of a flat screwdriver into the slot in the middle of the timer, and turn it (the slot will only move in one direction). If the timer activates the switch for the heater, you’ll hear a click. But if the heater doesn’t engage when you do this, or the timer doesn’t start subsequently moving on its own, you need a new timer.
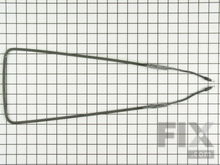
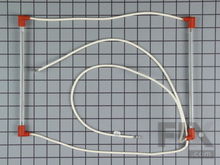
Defrost Heater
During the defrost cycle, the defrost heater thaws the frost and ice off the evaporator coils. Some evaporators have several heaters on them. A defrost heater is composed of a wire inside an aluminum or glass tube, under and next to the evaporator coils. Unplug the fridge and remove the evaporator cover from the back of the freezer compartment. Then locate the heater tube(s) and perform a multi-meter test for continuity.
Defrost Termination Thermostat
If your refrigerator is running too long, it could be due to a malfunction of the defrost termination thermostat. This is the component in charge of turning off the defrost heater at the end of the defrost cycle, when the evaporator gets up to 35 to 47 degrees F. It can normally be found on the evaporator tubing. Its circuit will open when the temperature is above 35 – 47 degrees F, so you will only be able to perform a multi-meter check for continuity in an environment of that same temperature, with the fridge unplugged to eliminate the chance of electric shock. But if you have a recent model of fridge, the wiring diagram may inform you that your thermostat has an internal bias resistor so that you can test the thermostat and the heater itself. When checking the continuity, unplug the fridge and keep in mind: a correctly functioning heater circuit has -a high resistance when the heater works and the thermostat is open, -a low resistance when the heater works and the thermostat is closed, and -no continuity at all when the heater is open.
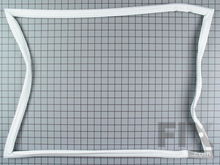
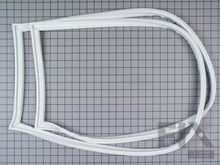
Refrigerator & Freezer Door Gaskets
Your refrigerator and freezer doors have a seal or gasket around the outside, made of vinyl and with an interior magnet so that the closed door is airtight. When the seal is not airtight, the fridge may be too warm, causing it to run longer than normally. You can determine if a damaged door gasket is the reason your fridge is running longer by checking for moisture on the freezer shelves, along the edge of the door, and in the area of the air outlet ducts. Verify that your gasket’s still uniform in shape, flexible, and uncracked. You can check the seal by closing the door on a piece of paper and pulling on the paper to see if the gasket’s holding it tight, as it should. Your door seal will last longer if you clean the gasket of spills or dirt every time it gets dirty. If a gasket needs to be replaced, you can make the job easier by running the new gasket, on low heat, in the clothing dryer so that it will be more flexible and easier to fit onto the fridge door.
Condenser Fan Motor
If your fridge is a newer frost-free model, it will likely have a condenser coil that’s kept cool with a fan. This fan keeps air moving to expel heat, so if it is not working right, the compressor has to run longer to cool the fridge. The tubes attached to the condenser also run in the space between the fridge and the freezer doors, so it that area feels warm, your problem could very well be the condenser fan. The condenser fan motor is usually on the bottom of the fridge near the back, conveniently close to the compressor. Start your inspection by unplugging the fridge and taking off the access panel at the back. The fan needs to move freely, so remove any rubbish that would block the blade’s movements. It’s a good habit to vacuum the area on a regular basis. Also check for wear on the motor or blades, or signs the motor has seized and must be replaced. If the blades or rubber mounting grommets are worn or damaged, switch them out for new ones. Plug the fridge back in and check if the condenser fan turns on when the compressor does. Have a service technician check that the fan motor terminals are getting electricity, the connections are tightly coupled, and that the motor has continuity and the correct voltage.
Evaporator Fan Motor
Is your freezer and your fridge getting warmer? Does it seem like the fridge is always cycling on or stays on longer than before? You may have a problem with your evaporator fan motor, which ventilates the evaporator coils during the periods the compressor runs. It is supposed to turn on when the compressor does, and you ought to be able to hear the fan in the freezer compartment, and feel the air moving in there. Unplug the fridge and take off the cover from the evaporator fan, located on the back side of the back panel of your freezer compartment. Is the fan clogged up with frost or ice? That means there’s a problem with defrosting. Is there damage to the fan blades, or are they loose? You will need to replace those. Use your multi-meter to check the motor to ensure continuity. Check to see if the motor shaft turns freely: if not, you may need to look into a new motor. If the cause of the problem still isn’t obvious, have a service technician in so that the power can be reconnected to isolate whether electricity is being fed to the motor. Don’t try this on your own, though, since live voltage is dangerous.
Sealed System
The sealed system is made up of the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and the tubes around them. Damage or malfunction to any of these parts could be the cause of the fridge running too long or not getting cold enough. The sealed system is not suitable for DIY repair because of the gasses contained there; a service technician must repair it.
More Repair Parts
Still not sure which part is broken? We can offer you custom troubleshooting help if you search with your model number.